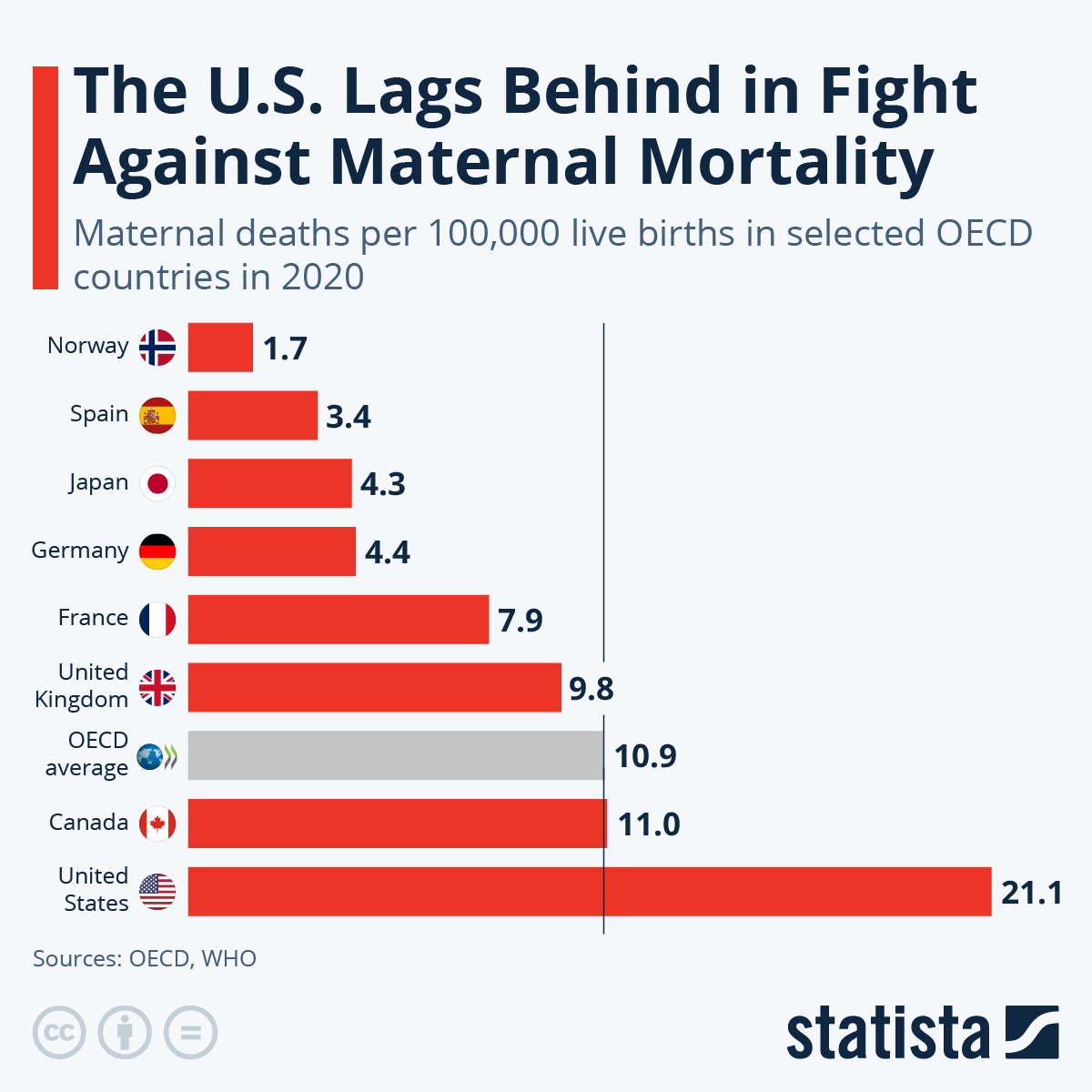
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. represent a growing public health crisis, particularly alarming as the country leads high-income nations in pregnancy-related deaths. A recent study highlighted that more than 80% of these deaths are preventable, yet the maternal mortality rate continues to climb, with disparities evident across various states, races, and ethnicities. The issue is compounded by insufficient access to prenatal and extended postpartum care, which are crucial periods for ensuring maternal health. Alarmingly, factors such as chronic medical conditions and systemic inequities contribute to this devastating trend. Addressing these maternal health disparities is essential for reducing maternal deaths and fostering a healthier society.
When examining the alarming trend of maternal fatalities in the United States, it becomes clear that these figures are indicative of broader issues within healthcare systems. The number of fatalities associated with childbirth reveals stark disparities in maternal wellness, influenced by a variety of factors, including economic inequalities and healthcare accessibility. Focusing on improving maternal care and support during and after pregnancy is critical in the fight against these preventable deaths. Moreover, the persistent racial and ethnic differences in health outcomes underscore the urgent need for comprehensive strategies aimed at bettering the conditions for all expectant mothers. To genuinely combat maternal mortality, targeted efforts to enhance healthcare resources, especially in underprivileged areas, will be key.
Understanding Maternal Mortality Rates in the U.S.
The maternal mortality rates in the United States have become a focal point of health discussions, particularly given that the country consistently ranks at the top among high-income nations in terms of pregnancy-related deaths. Recent studies indicate that from 2018 to 2022, U.S. maternal mortality rates rose significantly, underlining a troubling trend that seems to persist despite ongoing efforts to improve maternal health. With statistics showing preventable deaths account for over 80% of cases, policymakers are faced with a stark reality: the need for immediate reform and enhanced health services is paramount to mitigate these fatalities.
Data highlights disparities that exist across different racial and ethnic groups, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the most alarming rates of mortality. Such stark differences are not only deeply concerning from a health perspective, but they also reflect broader societal inequities on access to healthcare services. Addressing these disparities requires a multi-faceted approach that includes comprehensive reform of prenatal care, targeted interventions in maternal health education, and systemic policy changes to ensure equitable healthcare access for all demographic groups.
Factors Contributing to Rising Pregnancy-Related Deaths
The increase in pregnancy-related deaths has been attributed to a variety of factors, including chronic health issues that are becoming more prevalent among reproductive-age individuals. Conditions such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease are particularly concerning, with studies showing that these health issues are affecting younger women at alarming rates. Improper management of chronic conditions during pregnancy often leads to the escalation of complications that can result in preventable deaths, requiring more proactive and educated healthcare responses from medical professionals.
Additionally, the U.S. healthcare system’s fragmentation and lack of cohesive policies exacerbate these issues, creating maternity care deserts in several areas. As different states implement varying degrees of health policy reforms, these geographical discrepancies result in significant differences in maternal health outcomes. The need for uniform guidelines and accessible healthcare facilities across all states is critical to ensure that all pregnant individuals receive the level of care necessary to reduce mortality risks.
The Importance of Extended Postpartum Care
While maternal mortality is often examined during pregnancy and up to six weeks postpartum, a growing body of evidence suggests that the postpartum period should be extended to a full year. Research indicates that late maternal deaths, occurring between six weeks and one year after childbirth, account for nearly a third of all maternal deaths. Recognizing this extended timeline is essential for developing healthcare strategies that effectively monitor and support women’s health as they transition out of pregnancy.
Quality postpartum care that considers the long-term health of mothers can drastically reduce risks associated with preventable deaths. This includes regular follow-ups to manage chronic health conditions that may arise during or after the pregnancy period. Improving the continuity of care during this crucial phase is vital in ensuring mothers receive comprehensive support, thus lowering the likelihood of complications that could lead to serious health issues or fatalities.
Addressing Maternal Health Disparities
The persistent maternal health disparities among different racial and ethnic groups highlight the urgent need for focused interventions. Evidence suggests that addressing these inequities requires more than just policy changes; it calls for a systematic overhaul of the healthcare infrastructure that can better serve marginalized communities. This includes increasing access to culturally competent care, addressing biases within the healthcare system, and ensuring that all women receive adequate prenatal and postpartum support, regardless of their background.
Educational programs aimed at both healthcare providers and patients are essential in this fight against maternal health disparities. By promoting awareness around the specific needs and challenges faced by diverse populations, healthcare systems can better tailor their services, fostering an environment where all mothers have access to the same quality of care. Ultimately, reducing maternal mortality rates is intertwined with achieving health equity for all women.
Innovative Solutions for Reducing Maternal Deaths
To tackle the rising rates of maternal mortality, innovative solutions that extend beyond traditional healthcare models are necessary. This can include community-driven healthcare initiatives that empower local organizations to provide support, education, and resources focused on maternal health. Using data to identify high-risk areas and allocate resources effectively is crucial to ensure that vulnerable populations receive the targeted interventions they need before complications arise.
Moreover, integrating technology into maternal healthcare can help bridge gaps in access and education. Tools such as telehealth services can streamline communication between healthcare providers and patients, giving women the ability to seek help in real-time. By embracing these new approaches, the healthcare industry can cultivate a more proactive stance against the factors that contribute to maternal mortality, ultimately leading to better health outcomes for mothers across the nation.
The Role of Public Health Infrastructure in Maternal Care
Public health infrastructure is a critical component in addressing the increasing rates of maternal mortality. Investment in health tracking systems has become more essential than ever, especially with recent data collection efforts that began in 2018. As public health funding faces challenges, prioritizing maternal health can lead to significant improvements in how pregnancy-related complications are monitored and managed. Improved infrastructure will facilitate better data collection, enabling healthcare professionals to better understand the trends and barriers in maternal care.
Moreover, a robust public health system can help implement educational campaigns that inform expectant mothers about their rights and the importance of quality maternal care. By bridging the gap between mothers and the healthcare system, public health initiatives can enhance overall health outcomes by promoting preventive measures and timely interventions during pregnancy and beyond. Continuous investment in public health will ultimately play a fundamental role in reversing the rising trend of maternal mortality rates.
Improving Access to Quality Prenatal Care
Access to quality prenatal care is essential in reducing pregnancy-related deaths, yet many women face barriers that prevent them from receiving adequate care. Disparities exist not only by race but also by geography, with many communities lacking nearby facilities that offer comprehensive maternity services. By improving healthcare access, especially in rural and underserved areas, the chances for healthier pregnancies increase significantly. Ensuring that all women can access early and regular prenatal visits is key to addressing potential health risks proactively.
Policy changes that incentivize healthcare facilities to establish services in high-need areas can also provide relief. For example, telemedicine can make prenatal consultations more accessible, allowing women to receive needed care without the travel burden. By prioritizing equitable access to quality prenatal care, we can begin to see a shift in maternal mortality rates as more women are able to navigate their pregnancies in healthier conditions.
Educating Women on Maternal Health
Education plays a pivotal role in ensuring maternal health, as informed women are better equipped to make decisions regarding their pregnancies and postpartum care. Health education efforts should focus on understanding the signs of complications and the importance of seeking medical assistance promptly. Awareness programs tailored specifically for high-risk communities can help mitigate some of the factors that contribute to pregnancy-related deaths by empowering women with the knowledge they need to advocate for themselves and their health.
Incorporating maternal health education into school curriculums can also serve to create a well-informed future generation. By introducing concepts around reproductive health, pregnancy, and maternal rights early on, individuals can grow up understanding the healthcare landscape they will navigate. Lasting improvements can emerge from robust education systems championing maternal health topics, which can lead to lower mortality rates and healthier outcomes for mothers and their children.
The Link Between Chronic Conditions and Maternal Health
Chronic health conditions, such as hypertension and diabetes, have a significant impact on maternal health and can contribute to higher maternal mortality rates. The increase in reported cases of these conditions among younger women signifies a concerning shift that healthcare systems must address. Effective management of chronic conditions before and during pregnancy is vital for keeping mothers and their babies healthy. Early interventions, regular screenings, and personalized care plans can reduce acute risks during pregnancy that could potentially lead to severe complications.
Furthermore, integrating chronic disease management with prenatal care can create a more holistic approach to maternal health. Healthcare providers need to be equipped with tools and resources to effectively monitor these conditions in pregnant women. By turning attention to managing chronic diseases as an integral aspect of maternal care, providers will be positioned to lower both maternal morbidity and mortality, paving the way for healthier pregnancies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main factors contributing to high maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
The high maternal mortality rates in the U.S. are attributed to several factors, including a fragmented healthcare system, inequity in healthcare access, maternity care deserts, and ingrained biases across different racial and ethnic groups. Chronic health conditions, such as cardiovascular issues, also play a significant role in increasing pregnancy-related deaths.
How do maternal health disparities affect pregnancy-related deaths?
Maternal health disparities significantly impact pregnancy-related deaths, as evidenced by the higher mortality rates among American Indian, Alaska Native, and non-Hispanic Black women compared to their white counterparts. These disparities reflect deeper issues within the healthcare system and the need for targeted interventions to ensure equitable maternal healthcare for all racial and ethnic groups.
What role does postpartum care play in reducing maternal deaths?
Postpartum care is crucial for reducing maternal deaths, as nearly one-third of pregnancy-related deaths occur in the late postpartum period (42 days to 1 year after pregnancy). Improved continuity of care during this time can address complications arising from pregnancy and support maternal health, therefore decreasing overall maternal mortality rates.
Why has the U.S. maternal mortality rate continued to rise in recent years?
The U.S. maternal mortality rate has continued to rise due to various interconnected issues, including chronic health conditions becoming more prevalent among younger individuals, systemic healthcare inequities, and insufficient investment in maternal health services. The COVID-19 pandemic also exacerbated existing problems, contributing to a significant increase in mortality rates.
What can be done to effectively reduce pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
To effectively reduce pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., there must be increased investment in public health infrastructure, improved quality of prenatal and postpartum care, and policy changes that address systemic healthcare disparities. Understanding and replicating successful outcomes from states like California can guide strategies to improve maternal health across the nation.
What are ‘late maternal deaths’ and their significance in maternal mortality rates?
Late maternal deaths refer to those occurring between 42 days and 1 year post-pregnancy. Their significance lies in the need for comprehensive maternal healthcare that extends beyond the traditional six-week postpartum period. Recognizing these deaths highlights deficiencies in postpartum support and prompts the need for more substantial healthcare systems that encompass full recovery after childbirth.
How do racial disparities influence U.S. maternal mortality rates?
Racial disparities influence U.S. maternal mortality rates by resulting in significantly higher death rates among certain groups, particularly among American Indian, Alaska Native, and non-Hispanic Black women. These disparities stem from systemic inequalities in healthcare access, quality, and the impact of chronic health conditions, necessitating targeted policies to rectify these inequities.
What impact did the COVID-19 pandemic have on U.S. maternal mortality rates?
The COVID-19 pandemic had a notable impact on U.S. maternal mortality rates, particularly in 2021, where there was a sharp rise in pregnancy-related deaths. Factors contributing to this increase included healthcare system disruptions, rising chronic conditions, and overall stress on maternal healthcare services during the pandemic.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, rising from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2018 to 32.6 in 2022. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. |
| Racial Disparities | American Indian and Alaska Native women had the highest mortality rate at 106.3 per 100,000 live births. Non-Hispanic Black women followed at 76.9, with white women at 27.6. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The COVID-19 pandemic likely contributed to a sharp increase in maternal mortality in 2021. |
| Leading Cause of Death | Cardiovascular disease has replaced hemorrhage as the leading cause of pregnancy-related death, accounting for over 20% of deaths. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly one-third of total maternal deaths occurred between 42 days and one year postpartum, indicating a need for improved healthcare during the postpartum period. |
| Need for System Reforms | Investment in public health infrastructure and innovative solutions is urgently needed to address rising maternal mortality rates. |
Summary
Maternal mortality rates in the United States continue to rise alarmingly, marking a significant public health issue that needs immediate attention. Despite advancements in healthcare, the U.S. exhibits the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with many cases being preventable. The data clearly shows that there are disparities across racial lines, with minority groups facing disproportionately higher rates of death during or after pregnancy. This ongoing crisis highlights the urgent need for systemic reforms in prenatal and postpartum care, emphasizing the importance of addressing social determinants of health and ensuring equitable access to quality healthcare services for all mothers.