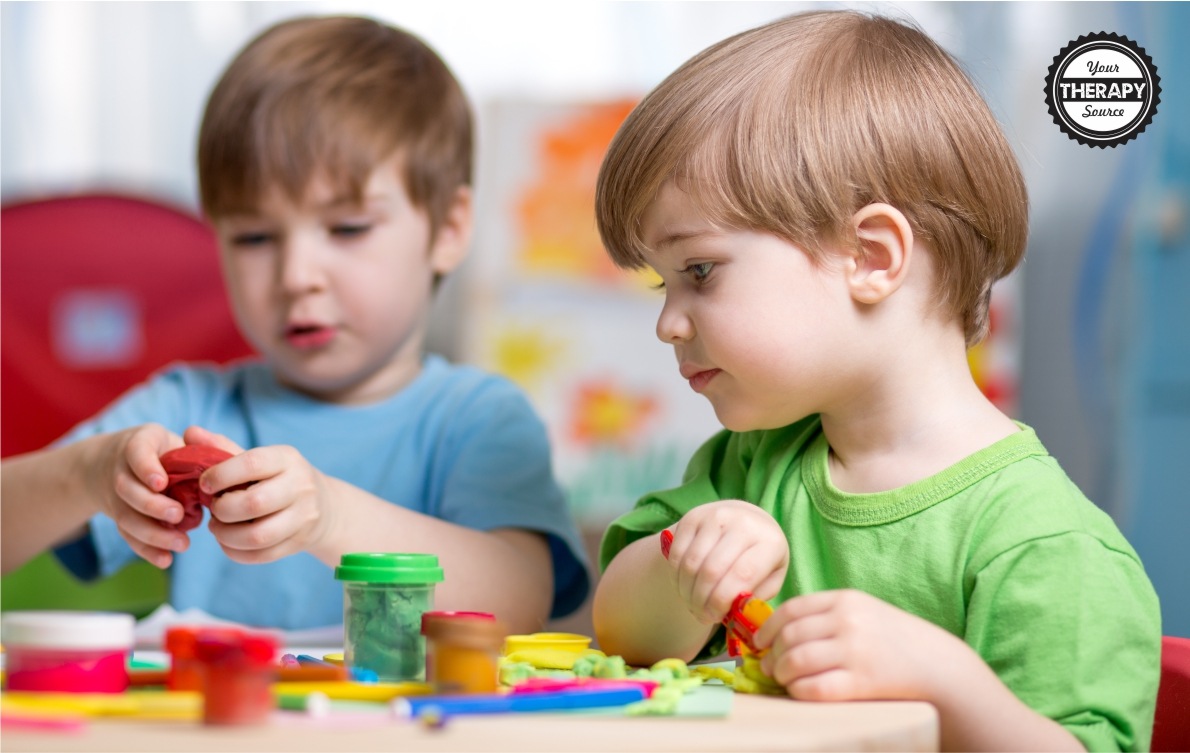
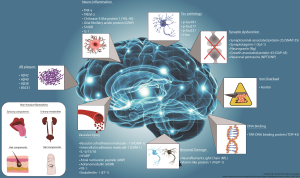
Social interaction needs are critical facets of human existence, as vital as food, water, and shelter. Recent studies emphasize the neurological basis of social connection, revealing how our brains are wired to engage with others. Researchers like Ding Liu have pinpointed the hypothalamic social circuit, which underscores the importance of social behavior in maintaining our mental health and well-being. Conversely, the detrimental effects of social isolation can lead to significant mental health challenges, making it crucial to understand this instinctive drive for companionship. As society continues to grapple with increased isolation, especially during times of crisis, recognizing and addressing our social interaction needs will be paramount for fostering healthier communities and relationships.
The necessity for human connection goes beyond mere preference; it is an essential requirement for psychological and emotional health. As we delve into the dynamics of social behavior, we uncover its profound relevance to our overall well-being. While feelings of loneliness can emerge from a lack of social engagement, research highlights the intricate link between our brain’s function and our socializing behavior. Understanding the neurological frameworks that support interaction, such as the hypothalamic mechanisms involved in social bonding, sheds light on why meaningful relationships are indispensable. This exploration of our social requirements provides an insightful lens into the struggles faced by individuals amidst the pervasive experiences of isolation.
The Neurological Basis of Social Connection
Recent research has illuminated the neurological underpinnings that drive our need for social connection, akin to basic physiological necessities like food and water. Studies have indicated that particular neuron circuits within the hypothalamus are integral in regulating social homeostasis. The activation of these neural pathways reflects our instinctual drive for companionship, highlighting how vital social interaction is for mental acuity and emotional stability. As social beings, our brains are wired in a manner that prioritizes social bonding, suggesting a biological imperative that extends beyond mere preference.
Connection and companionship not only enhance our emotional well-being but also manifest through various neural processes that contribute to our overall mental health. The research led by Ding Liu indicates that these connections can be biologically comparable to other essential needs, reinforcing the argument for viewing social behaviors through a lens of ‘social hunger’. Just as hunger motivates us to seek food, the need for social interaction compels us to nurture relationships, which are crucial for maintaining a balanced neurological state.
The Consequences of Social Isolation
The contemporary landscape has severely altered traditional forms of social interaction, with increasing numbers of individuals experiencing social isolation. This phenomenon, as noted by the U.S. Surgeon General, poses a significant threat to mental health, often leading to conditions that affect cognitive functioning and emotional stability. When deprived of social contact, individuals can experience a range of aversive experiences similar to hunger and thirst, suggesting that the effects of social isolation can manifest in both physical and psychological dimensions. Thus, understanding how isolation impacts neurological function is essential for developing effective strategies to combat loneliness.
Isolation not only hampers social behavior but can also contribute to long-term mental health issues. The research undertaken demonstrates that if social deprivation extends over time, individuals may develop aversive reactions toward social interaction, revealing the profound psychological consequences of sustained isolation. Enhancing public awareness about the significance of nurturing social bonds is crucial to mitigating these effects, as it can lead to improved interventions that promote healthier social environments.
The Importance of Social Behavior in Mental Health
Analyzing the role of social behavior in mental health underscores the necessity for interpersonal connections as a fundamental component of psychological well-being. Recent studies reveal that individuals facing mental health challenges, such as autism and depression, often struggle with engaging in meaningful social interactions. Understanding the neural mechanisms behind these behaviors can inform therapeutic approaches aimed at enhancing social skills and fostering connections, ultimately contributing to better mental health outcomes.
Moreover, the recognition of social behavior as a pivotal aspect of mental health emphasizes the interconnectedness between our social needs and neurological responses. Facilitating social interactions, especially in therapeutic settings, can help bridge the gap for individuals who experience difficulties due to their mental health conditions. This approach not only encourages community building but also enhances personal resilience, creating pathways for overcoming the adverse effects of isolation.
Exploring the Hypothalamic Social Circuit
The hypothalamus plays a crucial role in regulating both physiological and social needs, housing neuron circuits that are responsible for social bonding. This region of the brain not only governs fundamental survival drives but also influences our capacity to form and maintain social relationships. In Liu’s research, the discovery of specifically activated neurons during social seeking reinforces the essential connection between neural circuits and the innate drive for social interaction, further exemplifying how intertwined our physiological needs are with our social behaviors.
Investigations into the hypothalamic social circuit can lead to groundbreaking insights into how disruption of these neural pathways affects social abilities. By exploring these neural processes, researchers can better understand disorders characterized by social deficits, leading to targeted treatments aimed at restoring normal social functioning. Ultimately, this increases the potential for rehabilitation and support for individuals struggling with conditions that compromise their ability to engage socially.
Touch and Social Interaction Needs
Recent studies highlight the critical role of tactile interaction in fulfilling social needs, particularly regarding the impact of physical touch on emotional well-being. The preference for tactile stimuli, as observed in the research by Liu, suggests that touch serves as a key element in establishing and maintaining social connections. In humans, physical touch plays a significant role in nurturing relationships, enhancing emotional bonds, and facilitating non-verbal communication. Understanding the biological basis of these interactions can foster strategies to address the emotional ramifications of social isolation.
As society increasingly shifts towards digital interactions, understanding the role of touch becomes more vital. Liu’s research illuminates how our need for social contact may not be entirely satisfied through virtual means, suggesting that as interactions transition to screen-based platforms, the absence of physical touch can lead to heightened feelings of loneliness. Therefore, developing ways to incorporate tactile experiences into our interactions, even in a digital age, could help in mitigating the mental health effects of social isolation.
The Role of Sensory Inputs in Social Needs
Sensory experiences significantly shape our social interactions, as evidenced by experimental findings showing that even minimal sensory input can satisfy social needs. The research conducted by Liu illustrated that mice still exhibited stress and behavioral changes associated with social deprivation, even when they could hear or smell their peers but lacked direct contact. This indicates that sensory modalities such as hearing, sight, and particularly touch are vital in fulfilling our social instincts.
Understanding the sensory inputs that govern social behavior can have profound implications for human social dynamics. By exploring how sensory deprivation affects interpersonal relationships and social satisfaction, it may be possible to develop therapeutic avenues that enhance social engagement for those struggling with isolation. This insight further emphasizes the need for multidisciplinary approaches in addressing mental health issues rooted in social disconnection.
Implications for Human Behavior and Relationships
The insights drawn from animal studies regarding social behavior highlight the profound implications for understanding human relationships. As research indicates, the parallels between the social needs of mice and humans, including the biological mechanisms at play, underline a universal necessity for connection. This research can potentially inform interventions and support practices aimed at improving human relationships, particularly in our current society, which often elevates digital communication over face-to-face interactions.
Furthermore, recognizing how social needs influence our mental health instills greater urgency in addressing these issues on a broader societal scale. As researchers like Liu and Dulac work to unravel the complexities of social behavior and its neurological bases, the findings can translate into practical strategies for enhancing community support systems and fostering greater empathy and connectedness in everyday life. Ultimately, efforts to understand our social instincts not only inform psychological studies but also pave the way for healthier, more fulfilling relationships.
Addressing the Crisis of Social Isolation
The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated the crisis of social isolation, bringing national attention to the urgent need to address this public health concern. Social isolation has been linked to adverse effects on physical and mental health, prompting calls for greater awareness and intervention. By highlighting the neurological implications of social deprivation, researchers emphasize the importance of recognizing social connections as vital components of health, akin to food and water.
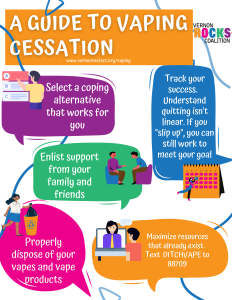
To combat the escalating rates of social isolation, communities need to create environments that facilitate interpersonal interactions. Initiatives like support groups, community events, and social outreach programs can go a long way in rebuilding social networks and reinforcing the biological need for connection. By investing in social infrastructures and recognizing the importance of social behavior, society can work towards minimizing the detrimental effects of isolation by promoting engagement and connectivity within communities.
Future Directions in Social Neuroscience Research
The field of social neuroscience is rapidly evolving, with ongoing studies aimed at uncovering the mechanisms that underlie social behaviors. Future research will likely focus on expanding our understanding of the hypothalamic social circuit and its implications for treating social behavior deficits. By integrating interdisciplinary perspectives, researchers can delve deeper into the biological, psychological, and social aspects of human behavior, ultimately enhancing our grasp of what drives social connectivity.
Moreover, as the relationship between social behavior and mental health continues to unfold, there will be significant opportunities to apply these findings in clinical settings. Understanding the neurological basis of social behavior will enable mental health professionals to tailor interventions that not only address individual needs but also prioritize social engagement as a therapeutic avenue. As these initiatives gain momentum, they will illuminate pathways to healthier communities and foster stronger interpersonal relationships.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the neurological basis of social connection and its impact on social interaction needs?
The neurological basis of social connection is rooted in specific neural circuits within the brain, particularly in the hypothalamus, which regulates both social behavior and essential physiological needs such as hunger and thirst. Understanding this connection sheds light on how our brain encodes the need for social interaction, similar to other basic needs, emphasizing that fulfilling social interaction needs is crucial for mental health.
How does social isolation affect mental health and social needs?
Social isolation has profound effects on mental health, often leading to increased feelings of loneliness, anxiety, and depression. Research indicates that prolonged isolation can adversely modify the desire for social interaction, making individuals less inclined to seek companionship. This highlights the importance of addressing social needs as part of mental health care, as fulfilling these needs can improve overall wellbeing.
What is the importance of social behavior in fulfilling social interaction needs?
Social behavior plays a vital role in fulfilling our social interaction needs. Engaging in meaningful social interactions is linked to emotional satisfaction, stability, and overall mental health. Studies reveal that positive social behaviors release neurochemicals like oxytocin and serotonin that foster feelings of connection, underscoring the significance of nurturing our social environments for psychological wellness.
How does the hypothalamic social circuit contribute to our understanding of social interaction needs?
The hypothalamic social circuit helps researchers understand the biological mechanisms that drive our need for social interaction. By studying this circuit, scientists have discovered neurons that govern the urge to seek companionship, especially when experiencing social deprivation. This insight reinforces the concept that social connection is as fundamental as other physiological needs, such as hunger and hydration.
What are the implications of research on social connection for addressing social interaction needs in humans?
Research on social connection has significant implications for how we understand and address social interaction needs in humans. By elucidating the biological and neurological factors governing social behaviors, stakeholders can develop interventions aimed at reducing social isolation and enhancing social interactions, which are crucial for mental health and community wellbeing.
Why is touch considered an important modality for satisfying social interaction needs?
Touch is recognized as a crucial modality for addressing social interaction needs because it enhances feelings of connection and comfort. In both animal studies and human behavior, tactile interactions—such as hugging or handshaking—have been shown to fulfill social needs effectively. This underscores the importance of physical contact in maintaining mental health and strong social bonds.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Social Interaction as a Basic Need | Health professionals view social contact as essential as food and water. This view was reinforced by the U.S. Surgeon General’s emphasis on social isolation as a public health concern in 2023. |
| Neurological Basis of Social Needs | Research reveals how the brain encodes the instinct for social interaction, exploring neural circuits and their dynamics in response to social deprivation and satisfaction. |
| Study Methodology | In isolation experiments with mice, researchers identified neurons active during social seeking and satiety phases. These findings indicated how isolation affects social behavior. |
| Touch and Social Interaction | Experiments highlighted the importance of touch as a sensory input that fulfills social needs, suggesting it plays a significant role in social behavior. |
| Implications for Humans | The findings have implications for understanding human social needs, especially in an era dominated by digital interactions, emphasizing the importance of tactile experiences. |
| Future Research Directions | Further study of social interaction’s impact on mental health can provide insights into improving relationships and overall wellbeing. |
Summary
Social interaction needs are crucial elements for human wellbeing, akin to the fundamental essentials of food and shelter. Recent research underscores the urgency of understanding these needs from a neurological perspective. By investigating the brain mechanisms that drive our desire for social contact, we can better comprehend how social interactions impact our mental health and relationships. This understanding is especially pertinent today, as many individuals experience heightened social isolation due to the prevalence of digital communication, highlighting the importance of re-establishing physical connections to enrich our lives.