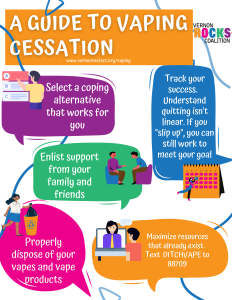
The prospective payment model is a transformative approach designed to address the financial challenges plaguing primary care in the U.S. By shifting payment structures, it aims to enhance primary care reimbursement, particularly through innovative frameworks like ACO PC Flex. This new model encourages healthcare financing solutions that build stronger incentives for preventative care, thereby reducing hospital visits and costs. As primary care faces increasing demand and a shortage of providers, this model positions accountable care organizations to offer broader and more efficient care options. Ultimately, the prospective payment model seeks to create a sustainable and patient-centered ecosystem within primary healthcare.
In recent years, the landscape of healthcare reimbursement has evolved, and alternative payment structures are gaining prominence. The forthcoming adjustments in financial models, particularly with initiatives like the ACO PC Flex, signal a shift towards more equitable compensation practices for primary care providers. Emphasizing preventative care incentives, these frameworks aim to alleviate the burden on clinicians while enhancing patient outcomes. As accountable care organizations take center stage, the focus is on fostering a more effective healthcare system that prioritizes patient health and sustainable practice finances. This shift not only addresses current market demands but also paves the way for a more resilient healthcare infrastructure.
Understanding the Prospective Payment Model in Primary Care
The prospective payment model represents a significant shift in the way primary care physicians are reimbursed for their services. Unlike traditional models where payments are made after services are rendered, prospective payment provides healthcare systems with funds upfront. This innovation is designed to alleviate the financial strain on primary care physicians, allowing them to invest in preventative care measures that could reduce hospital admissions and enhance patient care overall. Such a model encourages a proactive approach to health management, making it essential for a sustainable healthcare system.
By adopting the prospective payment model, primary care providers can allocate resources towards maintaining and improving patient health rather than merely reacting to acute medical situations. This shift can lead to better health outcomes, as providers are rewarded for prioritizing patient wellness through regular check-ups, screenings, and chronic disease management. Ultimately, this model aims to create a more efficient healthcare system, focusing on preventative care rather than costly interventions.
Challenges with Current Primary Care Reimbursement Models
Primary care reimbursement in the United States poses significant challenges for healthcare providers. A prevailing issue is the disproportionate compensation compared to specialty care, leading to burnout among primary care physicians who are often overburdened with patient volumes yet underpaid. This model, which favors specialists, does not sufficiently recognize the critical role of primary care in managing overall health outcomes. Moreover, the current fee-for-service model incentivizes higher volumes of care without necessarily improving quality, contributing to a crisis within the primary care sector.
Additionally, the existing reimbursement structure fails to encourage preventative care, often viewed as a lesser priority in comparison to immediate medical needs. With reimbursements primarily based on services rendered, physicians face disincentives for investing time in preventative strategies that can avert more serious health issues. A comprehensive change in the reimbursement model is crucial to ensure primary care is valued for its preventive capabilities and its importance in managing population health.
The Role of Accountable Care Organizations in Healthcare Financing
Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs) play a vital role in transforming healthcare financing by promoting efficiency and quality in care delivery. The concept behind ACOs is to encourage primary care providers to deliver high-quality care while simultaneously controlling costs. By aligning financial incentives with patient outcomes, ACOs facilitate collaboration between various healthcare providers to ensure patients receive comprehensive and coordinated care, reducing the likelihood of unnecessary hospitalizations and associated costs.
Furthermore, ACOs introduce a shared savings approach that benefits both healthcare providers and patients. When an ACO effectively manages costs and stays under a predetermined budget, the savings are distributed among providers as incentives, encouraging a focus on preventative care measures. By implementing these structures, the ACO model aims to make healthcare financing more sustainable and equitable, especially as it pertains to primary care services.
Incentives for Preventative Care through ACO PC Flex
The ACO PC Flex initiative introduces a pivotal change in how primary care providers are incentivized to deliver care. By increasing upfront payments to primary care practices, this model allocates significant resources toward preventative care efforts. This is instrumental in creating a healthcare environment where physicians are encouraged to invest time and effort in services that maintain patient health and prevent diseases before they escalate into critical issues.
Moreover, ACO PC Flex addresses a long-standing financial challenge by ensuring that costs related to delivering preventative services do not count against the provider’s budget thresholds. This innovation not only empowers primary care practitioners but also fosters a culture that values preventative care as an essential component of the healthcare system. Such advancements have the potential to substantially alter the landscape of primary care reimbursement, focusing on health outcomes rather than service volume.
How ACO PC Flex Could Revolutionize Primary Care
The implementation of ACO PC Flex offers a revolutionary approach to primary care by enabling a sustainable financial framework for providers. The upfront payment structure allows practices to invest in their infrastructure, enhancing their ability to provide a broader range of services that are essential for effective patient care. It represents a paradigm shift away from reactive treatment models towards a more proactive one that prioritizes patient wellbeing through comprehensive healthcare solutions.
If successful, ACO PC Flex could be a template for future primary care reimbursement models beyond Medicare, potentially influencing Medicaid and commercial insurance practices. By demonstrating that investment in primary care reduces overall health costs and improves patient outcomes, this model has the potential to reshape the financial landscape of healthcare financing as a whole, encouraging more equitable payment practices across all levels of care.
The Future of Primary Care Reimbursement Negotiations
As healthcare continues to evolve, the question of how primary care providers will be compensated remains critical. The traditional negotiations surrounding reimbursement rates have often left primary care underfunded, especially compared to specialty services. With initiatives like ACO PC Flex emerging, there is a hopeful indication that future reimbursement negotiations will prioritize the essential role of primary care in the healthcare ecosystem. Advocating for a more equitable distribution of funds, these negotiations could lead to improvements in pay and resources made available to primary care practitioners.
Furthermore, as discussions regarding healthcare financing take place, the voice of primary care needs to be amplified. Engaging with policy makers and stakeholders to advocate for reimbursement structures that reflect the true value of primary care is paramount. Empowering primary care providers will not only enhance their compensation but ultimately lead to a more efficient and effective healthcare system that benefits all patients.
Addressing the Demand for Primary Care Services
The growing demand for primary care services is an urgent issue facing the U.S. healthcare system. With more individuals seeking regular healthcare services than ever before, the strain on primary care providers is palpable. This increasing demand has highlighted the need for innovative solutions, such as ACO PC Flex, which aims to bolster funding and support for primary care, ensuring that practitioners can adequately meet patients’ needs.
The shift towards preventative care, supported by enhanced reimbursement models, also plays a critical role in addressing this rising demand. By focusing on early detection and management of health conditions, primary care can alleviate the pressure on emergency services and specialists, ensuring a more balanced healthcare ecosystem. This proactive approach not only supports patient health but also improves overall system efficiency.
The Impact of Preventative Care Incentives in Primary Care
Preventative care incentives have become increasingly vital in the discussion about primary care reimbursement and overall healthcare outcomes. By providing financial rewards and resources for preventative measures, ACO PC Flex encourages primary care practitioners to focus on keeping patients healthy, rather than merely treating illnesses. These incentives can manifest in various forms, such as additional funding for health screenings or programs aimed at managing chronic diseases effectively.
Moreover, integrating preventative care into the primary care framework helps to educate patients on health management and promotes healthy lifestyle choices. This proactive approach has the potential to reduce healthcare costs significantly over time by minimizing the need for more expensive interventions and treatments. Ultimately, a focus on preventative care can lead to healthier communities and a more sustainable healthcare infrastructure.
Exploring Innovations in Healthcare Financing
Innovations in healthcare financing, such as those introduced through ACO PC Flex, are crucial to reshaping the landscape of primary care. As the traditional models of reimbursement evolve, there is an increased emphasis on integrating financial sustainability with quality patient care. These advancements signal a shift towards understanding the long-term benefits of investing in primary care—prioritizing not just treatment but also the maintenance of health.
Additionally, the emphasis on creating more inclusive financing models that support both Medicare and Medicaid patients exemplifies a growing acknowledgment of the diverse needs within the U.S. healthcare system. Exploring and promoting these innovations can lead to better policy decisions and, ultimately, improved health outcomes for all populations, particularly those in need of comprehensive primary care services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Prospective Payment Model in primary care reimbursement?
The Prospective Payment Model is a healthcare financing strategy where payments to providers are made in advance for expected services, rather than after services are delivered. This model aims to help providers, especially within accountable care organizations (ACOs), receive higher upfront payments to enhance primary care delivery and incentivize preventative care.
How does ACO PC Flex relate to the Prospective Payment Model?
ACO PC Flex is a new initiative that utilizes the Prospective Payment Model to increase upfront primary care payments. By providing a large payment prior to delivering services, it encourages providers to focus on preventative care and keep patients out of hospitals, promoting better health outcomes and managing costs effectively.
What challenges does the Prospective Payment Model address in primary care reimbursement?
The Prospective Payment Model tackles issues such as low reimbursement rates for primary care practitioners compared to specialists. By offering advance payments, it alleviates financial pressures on primary care providers, incentivizing them to invest more time in patient counseling and preventative care, rather than just focusing on volume.
How can the Prospective Payment Model improve healthcare financing for primary care?
By transitioning to a Prospective Payment Model, healthcare financing can become more stable for primary care providers. This model prioritizes upfront payments based on average county costs, creating viable funding opportunities that enable practices to expand services and focus on maintaining patient health outside traditional office visits.
What incentives does the Prospective Payment Model create for preventative care?
The Prospective Payment Model incentivizes preventative care by rewarding primary care physicians with upfront payments that do not count against their costs when providing additional services. This setup encourages doctors to invest in patient health proactively, reducing the likelihood of serious illnesses and costly hospitalizations.
Could the Prospective Payment Model replace traditional reimbursement methods in primary care?
If the Prospective Payment Model, as tested in initiatives like ACO PC Flex, proves successful, it has the potential to influence traditional reimbursement methods in primary care. Positive outcomes in managing costs and improving patient health could lead to broader adoption among private insurance companies and Medicaid.
What role do accountable care organizations play in the Prospective Payment Model?
Accountable care organizations (ACOs) are crucial to the Prospective Payment Model as they implement the framework of shared savings and upfront payments. ACOs aim to manage patient care efficiently, and the Prospective Payment Model within ACOs helps them offer comprehensive preventative services while focusing on cost reduction.
How might the Prospective Payment Model affect patient access to primary care?
By enhancing financial stability and incentivizing preventive services, the Prospective Payment Model may improve patient access to primary care. Increased upfront funding allows providers to allocate resources to maintain patient relationships and tackle health issues before they require more intensive, costly interventions.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Care Crisis | U.S. primary care is facing a crisis due to rising demand and a shortage of doctors. |
| ACOs | Accountable Care Organizations aim to incentivize quality care at lower costs while sharing savings with providers. |
| Prospective Payment Model | Under ACO PC Flex, payments are made before services are delivered, which can encourage productive healthcare practices. |
| Increased Funding | The model plans to provide significantly higher payments to primary care providers compared to historical levels. |
| Preventative Care Focus | Encourages spending time on preventive measures to avoid serious illnesses and reduce hospital visits. |
Summary
The prospective payment model represents a transformative approach in U.S. primary care, addressing critical funding issues and the need for innovative healthcare delivery methods. Through the implementation of ACO PC Flex, the focus shifts towards incentivizing preventive care and effective management of patient health, thereby creating a sustainable cycle of improvement in primary care services. If successful, this model has the potential to reshape how primary care is financed and enhance patient care across the healthcare system.