Stem cell therapy for eye treatment represents a groundbreaking advancement in the field of ophthalmology, specifically for patients suffering from corneal damage. Recent clinical trials at Mass Eye and Ear have highlighted the effectiveness of the cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC) procedure, which utilizes limbal stem cells from a healthy eye to promote corneal repair. This innovative therapy has demonstrated over 90 percent success in restoring the cornea’s surface, providing new hope for vision restoration in individuals with previously untreatable conditions. The ability to regenerate corneal tissue not only alleviates persistent pain but also significantly improves visual acuity, making it a crucial development in eye care. As research continues, the potential for expanding this treatment to a broader range of patients becomes increasingly promising.
The innovative approach to eye care via cellular therapies marks a transformative shift for individuals facing severe vision impairments. Techniques involving the use of limbal stem cells are being explored as a solution for corneal injuries that were once deemed irreparable. Known for their role in maintaining a healthy corneal surface, limbal stem cells are now being harvested and refined through advanced procedures like CALEC, set forth by pioneering institutions such as Mass Eye and Ear. These advancements promise not only structural restoration of the eye but also significant improvements in overall visual performance. As further studies validate the safety and efficacy of these procedures, we anticipate a new era of ophthalmologic treatments that could redefine standards in vision correction.
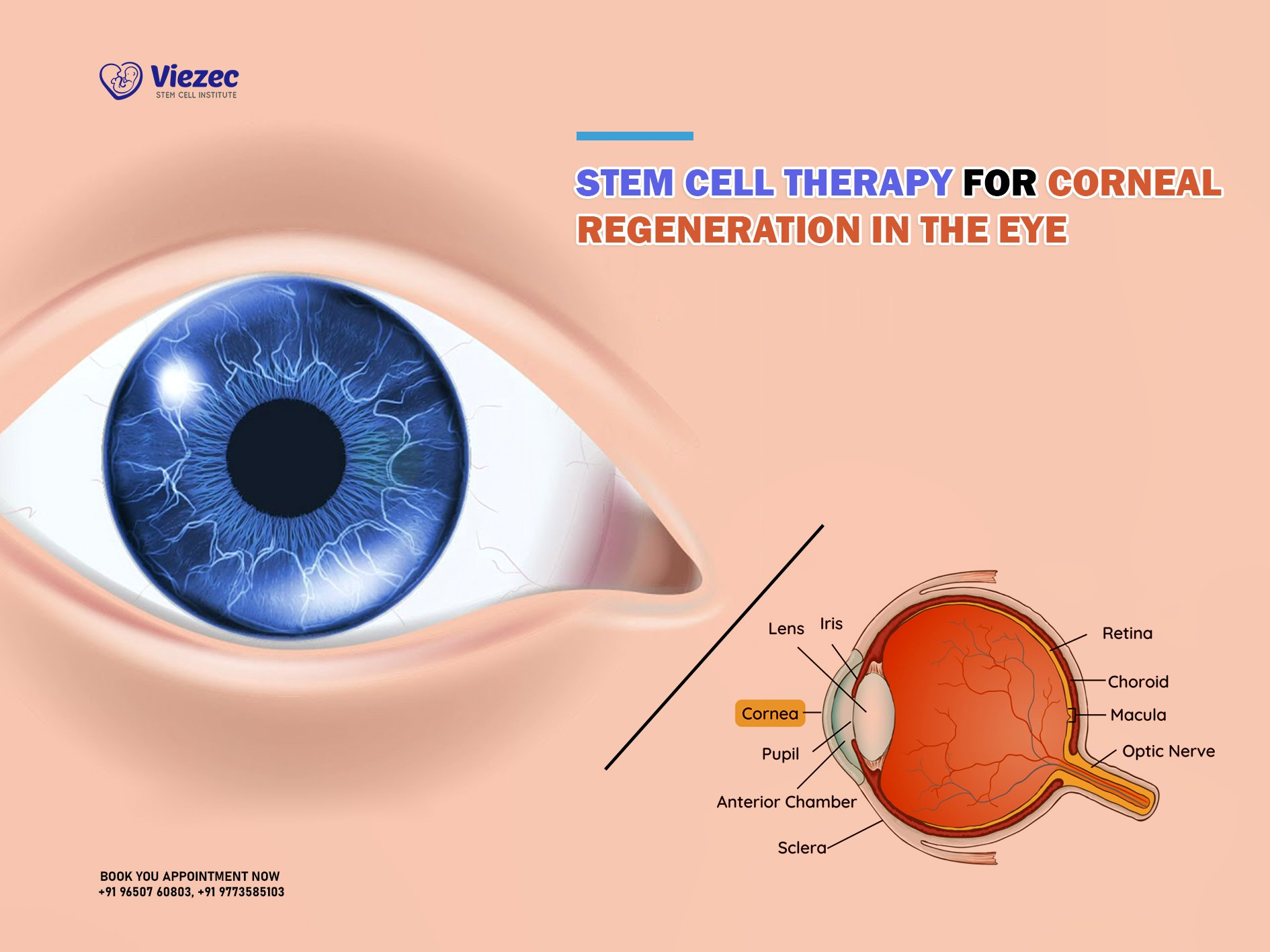
Understanding the CALEC Procedure for Corneal Repair
The CALEC procedure, or Cultivated Autologous Limbal Epithelial Cells, represents a groundbreaking approach in the preservation and restoration of corneal health, particularly for patients suffering from severe corneal damage. This innovative treatment is conducted at Mass Eye and Ear, where leading ophthalmologists utilize healthy limbal stem cells from the patient’s unaffected eye. By carefully extracting these cells and cultivating them into a graft, surgeons can then transplant this graft into the damaged cornea, promoting healing and surface reconstruction. The success of the CALEC process highlights not only advancements in medical technology but also the significant potential it holds for those with previously untreatable corneal injuries, such as those caused by burns or infections.
Researchers at Mass Eye and Ear, under the leadership of Ula Jurkunas and Reza Dana, have been able to achieve remarkable results with this technique. Combining rigorous preclinical research with established practices, they developed a consistent graft manufacturing process, which assures high-quality results necessary for effective treatment. During the clinical trials, evidence indicated that the CALEC procedure restored the corneal surface in 90% of participants, showcasing significant promise for those facing vision impairments due to corneal defects.
Moreover, the CALEC procedure’s innovative nature is complemented by its rigorous testing and monitoring protocols. Participants in the trial were carefully followed for 18 months, during which success rates continued to rise from initial assessments at three months to impressive figures at 12 and 18 months. Importantly, this technique not only restores physical integrity to the eye but has also led to tangible improvements in visual acuity for many participants, alleviating pain and restoring functionality that may have been compromised for years. As research continues, it is anticipated that CALEC will set a new standard for corneal repair while paving the way for further developments in stem cell therapies across eye care.
The Role of Limbal Stem Cells in Vision Restoration
Limbal stem cells are essential for maintaining the health and transparency of the cornea, making them a focal point in the pursuit of effective treatments for corneal injuries. These specialized cells reside in the limbal region and play a pivotal role in regenerating the epithelial layer of the cornea, which can be critically impaired in cases of injury or disease. When the limbal stem cells are damaged or deficient, patients often face debilitating conditions such as chronic pain, persistent redness, and significant vision loss, rendering them unable to undergo traditional corneal transplants. Understanding the restoration of these stem cells through novel techniques like the CALEC procedure is crucial for advancing eye care.
Researchers have documented that with the CALEC approach, extracted limbal stem cells can be effectively multiplied and transplanted to repair damaged corneal surfaces, offering hope to patients with serious vision challenges. The outcomes of the recent clinical trials not only validate the effectiveness of limbal stem cells in regaining corneal functionality but also set the stage for potential future applications in treating other ocular conditions. As the body of research on limbal stem cell applications expands, the potential for these therapies to revolutionize ocular health and vision restoration continues to grow, underlining the significance of understanding and harnessing the power of these unique cells.
Innovations in Stem Cell Therapy for Eye Treatment
Recent advancements in stem cell therapy have catalyzed a paradigm shift in how ocular diseases, particularly those affecting the cornea, are approached. The CALEC procedure exemplifies such innovation; it transforms how we view corneal repair by employing the patient’s own limbal stem cells, thereby minimizing rejection risks and enhancing healing outcomes. This cutting-edge methodology has emerged from years of research and collaboration between various institutions, including Dana-Farber and Mass Eye and Ear, reflecting a holistic approach to solving complex problems in eye care. As the first human trial of its kind in the United States, this procedure not only holds implications for corneal restoration but also serves as a pioneering step towards broader applications of cellular therapies in various areas of ophthalmology.
The success rates exhibited by the CALEC procedure not only underscore its efficacy but also highlight the importance of personalized medicine. By tailoring treatment plans to utilize the patient’s own biological materials, researchers could greatly enhance recovery rates and minimize the chances of adverse reactions. Additionally, future research may pave the way for altering the procedure to accept donor limbal stem cells, significantly broadening the patient demographic eligible for such life-altering treatments. As studies continue and approval progresses, stem cell therapy could become a cornerstone method for treating a wide array of visual impairments, enhancing the quality of life for countless individuals suffering from corneal injuries.
Future Perspectives on Stem Cell Treatments for Eye Conditions
The ongoing research into stem cell therapies, particularly within the realm of ocular health, heralds a promising future for patients with eye conditions that were once considered untreatable. The successes observed in the CALEC trials provide a solid foundation upon which to build further studies, which will aim to verify and expand the benefits of this innovative procedure across diverse populations. Future research endeavors are anticipated to involve larger patient cohorts and multi-center trials, enhancing the statistical validity and generalizability of findings. Such expansions are critical for informing best practices and ensuring as many patients as possible have access to these transformative therapies.
Moreover, the insights gained from the CALEC procedure shall likely guide research interests in developing allogeneic options that could utilize donor limbal stem cells. Such initiatives would remove the restriction of needing an unaffected eye for the harvesting of stem cells, thereby facilitating treatment for patients with bilateral corneal injuries. As the scientific community rallies around stem cell technology, the dream of effectively treating various forms of eye damage and restoring vision is edging closer to reality, potentially revolutionizing the way we address ocular health and healing.
The Clinical Impact of the CALEC Procedure
The CALEC procedure has displayed significant clinical impact, as evidenced by the remarkable outcomes observed in the 14 patients who were part of the clinical trial at Mass Eye and Ear. Over the course of the study, a comprehensive evaluation of visual acuity revealed that participants experienced substantial improvements, with many achieving healing rates of up to 93%. Such statistics not only illuminate the efficacy of the technique but also reveal a profound relief in patient symptoms, allowing individuals who had suffered from chronic corneal injuries to regain their quality of life. This successful application of stem cell therapy underscores the potential for personalized treatments that may reshape ophthalmic practices.
Post-surgical assessments further demonstrated that the CALEC procedure, being minimally invasive, has a favorable safety profile with only minor adverse outcomes reported. Given the scale of success in restoring corneal health and alleviating symptoms, this innovative approach appears to offer a viable alternative to traditional corrective procedures. As follow-up studies continue, there’s optimism that the findings will inform best practices for deploying stem cell therapies effectively across various ocular conditions, thereby increasing access and enhancing treatment protocols for patients globally.
The Role of Research Collaborations in Advancing Eye Care
Collaborative efforts among leading research institutions and healthcare facilities have been pivotal in advancing treatment protocols like the CALEC procedure. The partnership between Mass Eye and Ear and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute exemplifies how interdisciplinary teams can converge to tackle complex medical challenges. Such collaboration fosters an environment where innovative ideas thrive, enabling breakthroughs in how we approach eye care and rehabilitation. As institutions work together, they can draw on shared resources, knowledge bases, and technical skills, leading to more robust and comprehensive research outcomes.
These partnerships are not only beneficial for the research teams but also significantly impact patient care. By pooling expertise and resources, researchers can accelerate the pace of testing and validating new treatments, ensuring that more effective therapies reach patients more quickly. The hope is that successful collaborations establish a blueprint for future research initiatives, emphasizing the importance of teamwork in advancing healthcare technologies, especially in the realm of stem cell therapies. As exemplary partnerships flourish, the field of ophthalmology stands to benefit notably, expanding treatment options and improving patient outcomes in the long run.
Safety and Efficacy of Stem Cell Approaches in Eye Treatment
The safety and efficacy of stem cell therapies, particularly in the context of treating eye conditions, are paramount considerations for researchers and clinical practitioners alike. In the CALEC procedure trials, it was noted that complications were rare, with no significant adverse events occurring during the follow-up period. A solitary case of minor complications related to chronic factors like contact lens usage was reported, highlighting the importance of patient management post-surgery. These findings provide critical reassurance on the viability of stem cell interventions in clinical practice, allowing more practitioners to consider incorporating such innovative treatments into their therapeutic arsenal.
Moreover, the promising success rates noted during the studies have instilled confidence in utilizing stem cell therapies for ocular repairs. With over 90% efficacy in restoring corneal surfaces, the Therapeutics Research community envisions a future where stem cell interventions can become standardized treatments for various types of corneal trauma. Ongoing assessment of safety profiles will remain central to validating the long-term benefits of these procedures, ensuring they meet the rigor of regulatory expectations while providing patients with effective and safe treatment options.
Patient-Centric Approaches in Clinical Eye Trials
Patient-centric approaches have become crucial in designing and executing clinical trials for eye treatments like the CALEC procedure. Engaging patients as active participants in their treatment journey not only democratizes the process, but also ensures that their perspectives, needs, and experiences are being considered by the research teams. The collaborative nature of drawing insights from the patient experience helps refine research questions and protocols, yielding more applicable and relevant findings that resonate with the real-world experiences of those affected by ocular diseases.
Additionally, creating an environment where patients feel informed about their treatment options empowers them to make educated choices regarding their care. As seen in the CALEC trials, ongoing communication regarding progress, expectations, and outcomes significantly enhances the patient’s overall experience and adherence to treatment protocols. As the field of ophthalmology continues to evolve with advanced techniques like the CALEC procedure, maintaining a focus on patient-centered practices will be essential to nurturing trust, improving therapeutic efficacy, and ultimately leading to better healthcare outcomes.
Regulatory Pathways for Stem Cell Therapies in Eye Care
Navigating the regulatory landscape for new stem cell therapies, such as CALEC, is a critical aspect that can significantly impact the pace with which advancements reach clinical practice. The approval process for such innovative treatments requires a thorough examination of safety data, efficacy, and ethical considerations, guided by agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). As the landmark CALEC clinical trial has set a precedent as the first of its kind in the U.S., the results may forge a path for future therapies aimed at addressing various ocular conditions, while also providing a framework for regulatory guidelines for similar stem cell treatments.
Moreover, ongoing dialogues between researchers, regulatory bodies, and stakeholders will be essential in shaping the landscape for future approvals. Ensuring transparency in data sharing and addressing public concerns regarding the ethical use of stem cells will contribute to a more informed and receptive atmosphere regarding new treatments. As research progresses, regulatory pathways must remain adaptable to the evolving landscape of medical science, allowing for innovation while maintaining stringent oversight to protect patient health and welfare.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stem cell therapy for eye treatment and how does it work?
Stem cell therapy for eye treatment, specifically through procedures like the CALEC method, involves using cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells to repair damaged corneas. This innovative approach extracts stem cells from a healthy eye, expands them into a graft, and transplants them into the damaged eye to restore the cornea’s surface.
How effective is the CALEC procedure in restoring vision?
The CALEC procedure has shown over 90% effectiveness in restoring the cornea’s surface, with a significant portion of participants experiencing complete restoration within 12 to 18 months following treatment. This advancement marks a new hope for patients with previously untreatable cornea damage.
What are limbal stem cells and their role in stem cell therapy for eye treatment?
Limbal stem cells are crucial for maintaining the cornea’s smooth surface. In stem cell therapy for eye treatment, these cells are harvested from a healthy eye and used in procedures like the CALEC method to regenerate damaged tissue in the cornea, addressing conditions such as limbal stem cell deficiency.
Is the CALEC procedure available for patients with both eyes affected?
Currently, the CALEC procedure is only suitable for patients with one affected eye, as it requires a biopsy from the healthy eye to source the necessary stem cells. Future research aims to develop techniques that could enable treatment for those with bilateral eye damage.
What clinical trial results support the safety of stem cell therapy for eye treatment?
The clinical trial conducted by Mass Eye and Ear demonstrated that the CALEC procedure has a high safety profile. Out of 14 participants, there were no severe complications, and minor adverse events were quickly resolved, confirming the treatment’s feasibility and safety over an 18-month follow-up.
What advancements are being pursued in stem cell therapy for corneal repair?
Future advancements in stem cell therapy for corneal repair include exploring allogeneic manufacturing processes to use limbal stem cells from cadaveric donor eyes. This approach aims to expand treatment eligibility to patients suffering from damage in both eyes.
Who are the key researchers involved in developing stem cell therapy for eye treatment at Mass Eye and Ear?
Key researchers involved in the development of stem cell therapy for eye treatment at Mass Eye and Ear include Ula Jurkunas and Reza Dana, who have led the CALEC trials and contributed to translating laboratory techniques into clinical applications.
What is the expected timeline for the CALEC procedure to become widely available?
While the CALEC procedure has shown promising results, it remains experimental and will require further studies and trials before it can receive federal approval and become widely available in clinical settings across the United States.
What are the implications of stem cell therapy on the future of vision restoration?
Stem cell therapy, particularly through the CALEC procedure, holds significant promise for the future of vision restoration, potentially offering new hope to individuals suffering from severe corneal damage that traditional treatments, such as corneal transplants, cannot address.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Introduction of CALEC Surgery | First CALEC surgery performed at Mass Eye and Ear by Ula Jurkunas. |
| Clinical Trial Results | Safe restoration of corneal surfaces in 14 patients; 90% efficacy in restoring cornea. |
| Methodology | Utilizes stem cells from a healthy eye, expanded into a tissue graft over 2-3 weeks. |
| Patient Requirements | Patients must have only one affected eye for the procedure. |
| Success Rates | 50% complete restoration at 3 months; 93% success rates at 12 months. |
| Safety Profile | High safety profile reported; only one minor adverse event observed. |
| Future Research | Additional trials needed for FDA approval and to expand treatment options. |
Summary
Stem cell therapy for eye treatment has emerged as a groundbreaking solution for patients suffering from corneal damage that was previously considered untreatable. The cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC) surgery successfully restored corneal surfaces in a significant number of trial participants, proving its safety and effectiveness. As research continues, we look forward to the broader application of this innovative therapy, which could revolutionize eye care and restore vision for many more patients.