Bile imbalance linked to liver cancer has emerged as a critical area of research, revealing how the disturbance in bile acid production and regulation can lead to serious liver conditions, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the predominant type of liver cancer. Recent studies have uncovered a pivotal relationship between the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway and bile acid metabolism, highlighting the intricate mechanisms that contribute to cancer progression. Bile acids, once considered merely digestive agents, are shown to play significant roles in cellular signaling and metabolic regulation. The implications for liver cancer treatment are profound, as targeting the YAP FXR relationship could open new therapeutic avenues to correct bile imbalances and halt the development of cancer. As research delves deeper into bile acid dynamics, understanding this connection is vital for developing effective interventions against liver diseases.
The connection between bile production irregularities and liver malignancies is a burgeoning field of study. Disruptions in bile acid homeostasis can lead to not only inflammation but also to the progressive development of hepatocellular carcinoma, underscoring the need for innovative therapeutic strategies. Key molecular interactions, particularly involving the YAP and FXR axes, are central to comprehending how these metabolic disruptions influence cancer pathology. As bile acids transition from digestives to key metabolic regulators, their role in liver health cannot be overstated. This emerging knowledge sets the stage for targeted liver cancer therapies aimed at restoring normal bile acid functions.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Its Link to Liver Cancer
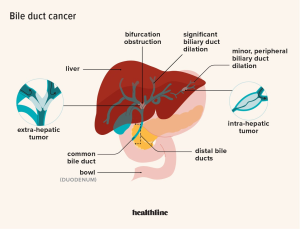
Bile imbalance is a critical factor in liver health, as bile acids play a vital role in digestion and metabolism. The liver produces bile, which is crucial for breaking down fats and absorbing fat-soluble vitamins. However, a disruption in the production or regulation of bile acids can lead to conditions such as fibrosis and inflammation, ultimately contributing to the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent research has uncovered the link between bile acid metabolism and the progression of liver diseases, highlighting the importance of maintaining a balanced bile composition for overall liver health.
In exploring the mechanisms behind bile imbalance, scientists have identified a molecular switch that can significantly influence bile acid levels. This switch involves the Hippo/YAP pathway, where the YAP protein, typically associated with promoting cell growth, paradoxically acts to repress bile acid function by interfering with the Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR). The suppression of FXR by YAP leads to an accumulation of bile acids in the liver, a pathway that has been recognized as a contributing factor to the development of liver cancer. This discovery paves the way for potential therapeutic interventions aimed at restoring bile acid homeostasis.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is bile imbalance linked to liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)?
Bile imbalance is a significant factor in the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Disruptions in the regulation of bile acids can lead to liver injury and inflammation, which are precursors to HCC. A recent study highlighted how the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway affects bile acid metabolism, with YAP acting as a repressor of FXR, a receptor essential for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. This leads to an accumulation of bile acids in the liver, promoting cancer development.
What role do bile acids play in liver cancer treatment and research?
Bile acids have a critical role in liver cancer treatment as they are involved in regulating metabolic processes within the liver. Research has shown that targeting bile acid metabolism via pathways like the YAP/FXR relationship could provide new therapeutic interventions for liver cancer. By enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion, it may be possible to reduce liver damage and inhibit cancer progression, presenting new avenues for liver cancer treatment.
What are the implications of the YAP FXR relationship in liver cancer?
The YAP FXR relationship has significant implications in liver cancer as it reveals a critical pathway that governs bile acid metabolism. YAP, when activated, suppresses the function of FXR, leading to bile acid overproduction and subsequent liver damage. Understanding this relationship opens up potential therapeutic strategies, such as pharmacological stimulation of FXR, to mitigate liver cancer risk associated with bile imbalance.
What experimental models have shown promise in treating liver cancer associated with bile imbalance?
Several experimental models have shown promise in addressing liver cancer linked to bile imbalance. Interventions that include activating FXR, inhibiting HDAC1 (which enhances YAP’s repressive activity), or increasing the expression of bile acid export proteins (BSEP) have all demonstrated a reduction in liver damage and cancer progression. These approaches highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting bile acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment.
How can bile acid metabolism be controlled to prevent liver cancer?
To prevent liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, controlling bile acid metabolism is crucial. This can be achieved by targeting key regulatory pathways, such as enhancing the function of FXR or promoting bile acid excretion. Strategies that inhibit the repressive action of YAP, which disrupts bile acid homeostasis, could also significantly reduce the risk of liver injury and subsequent cancer development.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | A significant imbalance in bile acids produced by the liver can initiate liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| Molecular Switch Identified | A key molecular switch, YAP, regulates bile acid metabolism affecting tumor formation and liver health. |
| Role of FXR | FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) is essential for bile acid homeostasis; its repression by YAP leads to bile acid overproduction and liver damage. |
| Potential Treatments | Interventions aiming to enhance FXR function or increase bile acid excretion may provide treatment avenues for liver cancer. |
| Research Support and Future Implications | The study, supported by NIH, indicates the need for further research on YAP’s role in metabolic regulation and liver disease treatment. |
Summary
Bile imbalance liver cancer is a growing concern within the medical community. The research indicates that disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to severe liver diseases, notably hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Understanding the molecular mechanisms, particularly the role of YAP in regulating bile acids and tumor growth, opens new avenues for potential treatments. By exploring pharmacological interventions that target FXR function, healthcare professionals may not only help manage but also prevent liver cancer caused by bile imbalance.