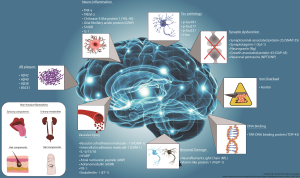
Learning and memory techniques are at the forefront of neuroscience research, offering excitement and hope, especially for addressing neurological disorders like dementia. Recent groundbreaking studies from Harvard highlight significant advances in understanding how memory formation occurs at the molecular level, focusing on synaptic plasticity—the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize. Insights gained from these techniques not only enhance our comprehension of memory but also promise new therapies for conditions marked by cognitive decline. As researchers investigate the intricate architecture of synapses, they unlock clues essential for developing interventions that could transform dementia research. This interdisciplinary approach between chemistry and neuroscience illustrates the power of innovative learning methods in deciphering the enigma of human memory and cognition.
The realm of cognitive enhancement and memory retention encompasses a rich variety of techniques and strategies designed to improve how we acquire and recall information. Known broadly as memory improvement methods, these practices are crucial, especially in the context of understanding complex mental processes involved in learning and remembrance. By exploring innovative approaches that illuminate aspects of synaptic communication, researchers can delve deeper into the fundamental mechanisms that shape our ability to remember. Such alternative terms as mnemonic devices, cognitive strategies, and neuroplasticity are vital in framing this discussion, revealing how emerging findings from Harvard neuroscience are set to redefine our grasp of memory retention and its underlying biology. Collectively, these methodologies represent an evolving narrative that intertwines scientific discovery with practical applications in education and mental health.
Advancements in Memory Formation Research
Recent breakthroughs in neuroscience have sharpened our understanding of how memories are formed and retained within the brain. The latest research conducted at Harvard has resulted in a revolutionary method that elucidates the molecular mechanisms underlying memory formation. This research provides critical insights into the synaptic plasticity—the robust process that allows neurons to strengthen their connections, which is vital for learning. By utilizing advanced techniques such as fluorescent labeling paired with high-resolution microscopy, researchers are able to observe the intricacies of synaptic behaviors, offering a glimpse into the neural networks responsible for memory.
Such advancements are not just academically intriguing; they bear significant implications for treating neurological disorders. As dementia and similar conditions are characterized by synaptic dysfunction, understanding the molecular basis of memory can guide the development of new therapeutic interventions. As noted by the lead researchers, including Adam Cohen and his team, these insights can potentially lead to groundbreaking treatments aimed at restoring synaptic integrity and, consequently, memory functions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the latest learning and memory techniques studied in relation to neurological disorders?
Recent advancements in learning and memory techniques, particularly from Harvard researchers, focus on the EPSILON method which maps synaptic plasticity—key to memory formation—in unprecedented detail. This innovative technique offers insights into the molecular foundations of learning and may inform therapies for neurological disorders such as dementia.
How does synaptic plasticity relate to learning and memory techniques?
Synaptic plasticity is crucial for learning and memory as it involves the strengthening and modulation of synaptic connections in the brain. Techniques such as EPSILON allow researchers to examine these synaptic changes with precision, advancing our understanding of how memories are formed and stored, which is vital in dementia research.
What is the significance of AMPARs in memory formation and learning techniques?
AMPARs, or alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors, are essential for synaptic plasticity. They play a critical role in memory formation by regulating synaptic transmission. Learning techniques informed by neurology are evolving to incorporate these insights, aiming to enhance cognitive abilities and address memory impairments.
How does Harvard’s research contribute to understanding memory formation in dementia research?
Harvard’s groundbreaking research, particularly with the EPSILON technique, sheds light on the synaptic behaviors linked to memory formation. By mapping molecular interactions at high resolution, the research offers potential pathways for developing treatments targeting synaptic dysfunction in dementia and similar neurological disorders.
What role does advanced microscopy play in studying learning and memory techniques?
Advanced microscopy techniques, as utilized in the EPSILON method, allow scientists to visualize and analyze the behavior of synaptic proteins that are crucial for learning and memory. This technology unlocks new possibilities in understanding the dynamic processes of memory formation and synaptic plasticity amidst challenges posed by neurological disorders.
Can learning and memory techniques be used to enhance cognitive function in everyday life?
Yes, understanding and applying techniques derived from neuroscience, such as spaced repetition and active recall, can enhance cognitive function and memory in daily tasks. Insights from research, such as that from Harvard, enable the development of strategies that leverage the brain’s natural synaptic plasticity for improved learning outcomes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Innovative Technique | Extracellular Protein Surface Labeling in Neurons (EPSILON) maps proteins involved in synaptic communication. |
| Research Importance | Provides insights that could lead to new therapies for neurological disorders like dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. |
| Synaptic Plasticity | The strengthening and modulation of connections between neurons, essential for forming memories. |
| Scientific Achievement | High-resolution observation of synaptic behavior, previously unachievable without invasive methods. |
| Future Research | EPSILON will facilitate studies on cognitive phenomena and enhance memory impairment therapies. |
Summary
Learning and memory techniques play a critical role in understanding how our brains process and retain information. The groundbreaking EPSILON technique developed at Harvard allows researchers to examine the molecular processes underpinning synaptic plasticity, which is fundamental for memory formation. This advancement not only sheds light on the intricacies of how memories are formed but also opens the door to developing new therapies that could significantly impact the treatment of conditions such as dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. By mapping the behavior of crucial proteins in synapses, this research paves the way for a deeper comprehension of cognitive functions, thereby revolutionizing the approach to learning and memory in both scientific and therapeutic realms.